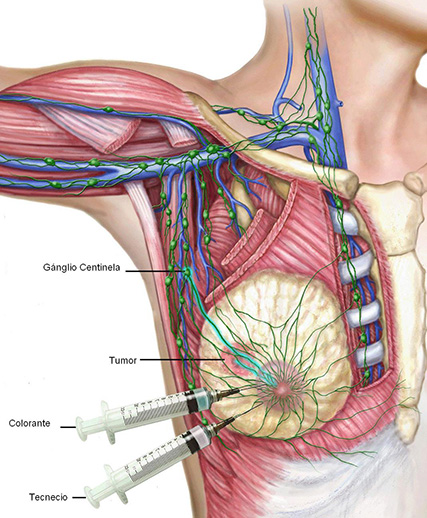
It is the removal of all the lymph nodes in the armpit. This gives us very precise information on the state of all the lymph nodes in the axilla, to know if they are invaded by tumor cells.
In addition to providing prognostic information, axillary lymphadenectomy continues to be the most effective method of controlling regional disease. Currently, it is continued when the sentinel node is positive and meets certain risk criteria.